Select your language

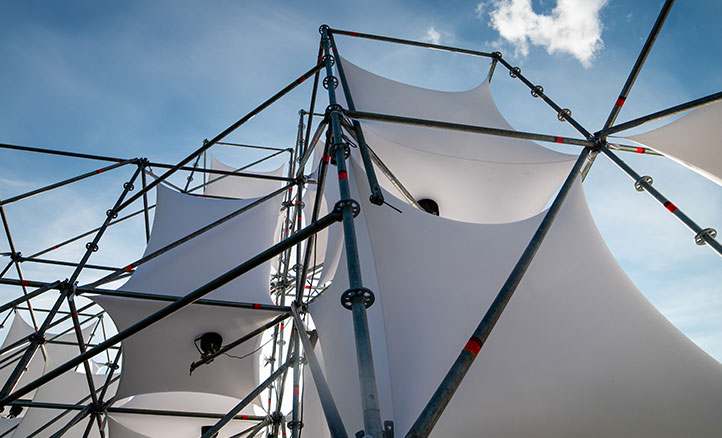
Membrane structures are lightweight architectural systems composed of tensioned membranes, such as PVC, polyester, or fiberglass. Primarily used for wide-span coverage in stadiums, exhibition centers, and swimming pools, they offer benefits like lightweight design, aesthetic appeal, and environmental sustainability. Their application continues to grow with material and technological advancements, expanding architectural possibilities. Design and construction require multidisciplinary expertise from structural engineers, architects, and material scientists to ensure safety, stability, and visual appeal.
