Tensegrity membrane structures use tensioned cables and supports to enable bold, stable designs. For large spans, cable-strut grids are preferred, offering enhanced performance and flexibility at a moderately higher cost.
选择您的语言

The membrane structure, also known as the tensioned membrane structure, is a novel architectural structure that emerged in the mid-20th century. In the 21st century, membrane structure architecture stands as one of the most representative and promising architectural styles. It breaks away from the traditional straight-line architectural style, presenting a refreshing sensation with its unique and elegant curved forms. The simplicity, clarity, and perfect combination of rigidity and flexibility, strength and beauty, provide architects with greater imagination and creative space. Based on their structural force characteristics, membrane structures can be broadly categorized into three types: tensioned membrane structures (cable-supported membrane structures), frame-supported membrane structures, and air-supported structures (inflatable membrane structures).
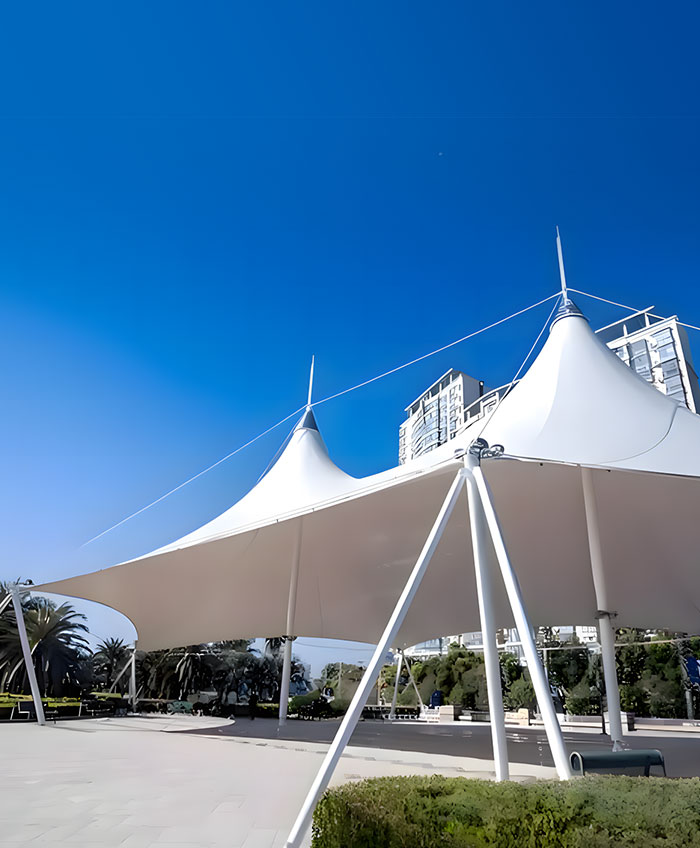

Tensegrity membrane structures use tensioned cables and supports to enable bold, stable designs. For large spans, cable-strut grids are preferred, offering enhanced performance and flexibility at a moderately higher cost.
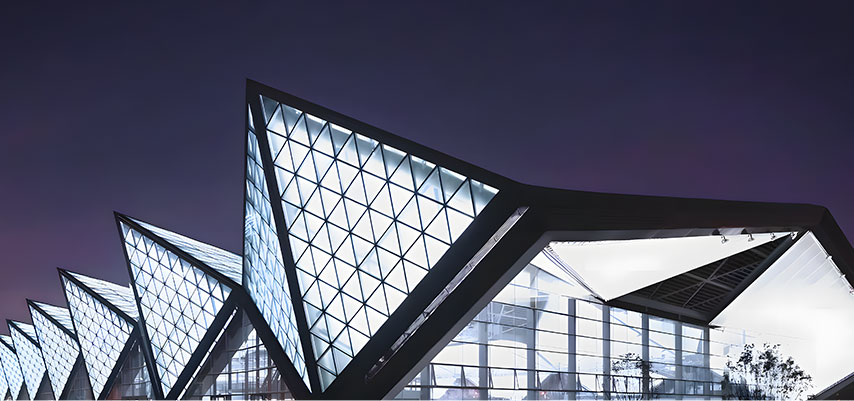

Frame-supported membrane structures use steel or laminated timber roof frames covered with tensioned membrane. Known for high stability, simple roof forms, unrestricted openings, and cost-effectiveness, they are widely suitable for spaces of all scales.
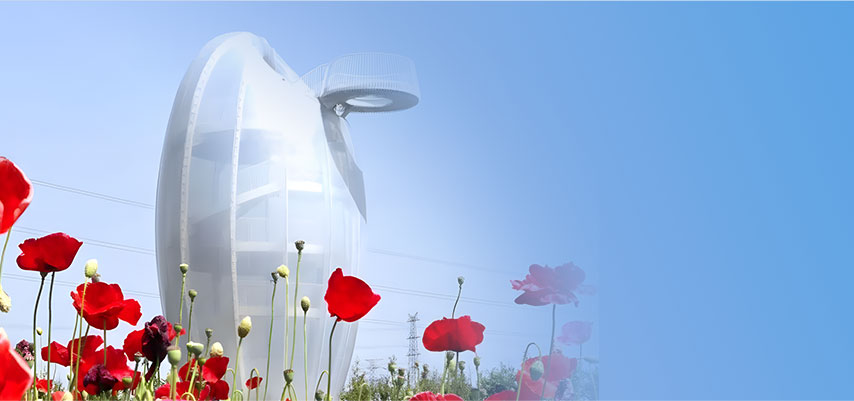

Pneumatic structures (air-supported/air-ribbed/inflated) include PVC air domes and ETFE cushions. ETFE cushions are popular for their lightweight, durable, and insulating properties in large-scale buildings.